Table Of Content

Embracing the following four beliefs is the first step in designing learning experiences that serve all students. Universal Design for learning is a set of principles that provide teachers with a structure to develop instructions to meet the diverse needs of all learners. UDL is similar to universal instructional design and universal design for instruction. All three advocate for accessible and inclusive instructional approaches that meet the needs and abilities of all learners.
Multiple Means of Engagement
UDL's implications stretch well beyond accommodating students with disabilities; it is a boon for all learners. By addressing the broad spectrum of engagement, representation, and comprehension, the UDL framework equips educators to craft a curriculum that meets diverse learning needs. At its core, UDL emphasizes the creation of instructional goals, methods, materials, and assessments that are inherently flexible. This adaptability ensures that learning experiences are tailored to the individual requirements of each student. Research on student learning demonstrates that multi-modal access helps to improve learning outcomes for all students. Multi-modal access essentially means providing several pathways to access course material.
Universal Design for Learning: Strategies in the Classroom
You don’t need specific tools or technologies to follow UDL’s principles either. Instead, your students choose from the tools and resources you already have. For strategic, goal-directed learners, differentiate the ways that students can express what they know.
Search Teaching Support and Innovation
Engagement strategies also include game-like elements and physical activities to sustain interest. It is through adherence to these principles that UDL successfully fosters an inclusive learning atmosphere where barriers are systematically identified and dismantled. Even if you’re not familiar with the term universal design, you’ve likely encountered many examples of it in your everyday life. Closed captions, automatic doors and accessibility features on smartphones are all examples of universal design. First-time registrants need to create a Professional Education account to register. We welcome participants who have a basic understanding of UDL, are eager to deepen their UDL practice, and are motivated to develop into UDL leaders at their schools.
By using Universal Design for Learning, all students can benefit from increased access to their course content, including many who are not registered to receive formal accommodations through the Disability Resource Center (DRC). Stigma, cost, and numerous other factors are barriers to registering with the DRC. As the COVID-19 pandemic has shown, all people are affected by changes to their environment, be it social or academic.
Forward Together: Helping Educators Unlock the Power of Students Who Learn Differently

Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is an educational framework that leverages scientific knowledge about human learning processes to create flexible learning environments. UDL aims to provide all students with equal opportunities to succeed by removing barriers and accommodating individual differences. To address the remarkable variability among students in today’s diverse learning environments, educators are increasingly turning to Universal Design for Learning (UDL). UDL offers a framework for guiding the design of learning opportunities that are inclusive and challenging for all learners. Equitable course development recognizes that students have a diverse range of abilities, environments, and experiences and incorporates multiple means of learning and expression for these students. By prioritizing accessibility in a course, instructors design their course from the vantage point of multiple perspectives, creating learning experiences that can engage a diverse group of students.
Teaching
New resource focuses on accessibility, universal design for learning - Nebraska Today
New resource focuses on accessibility, universal design for learning.
Posted: Fri, 20 Aug 2021 07:00:00 GMT [source]
For educators, this means designing lessons that are not overly complex or unnecessarily complicated. Whether a student is grappling with language barriers, learning English as a second language, or facing other language-related challenges, UDL strategies strive to make content accessible and engaging. Universal Design for Learning (UDL) takes a broad and inclusive stance toward education, recognizing the rich diversity of students' language skills. It acknowledges that learners come from a variety of linguistic backgrounds, each with unique challenges and abilities. Central to UDL is the goal of granting full access to learning for every student, a goal that is especially pertinent when it comes to language. It offers a trio of learning modalities--multiple means of representation, expression, and engagement--that are central to its customized approach.
Differentiated Instruction Made Practical
• Allow students to show what they know through a variety of formats, such as a poster presentation or a graphic organizer. Watch a video of what UDL looks like in the fifth-grade classroom of Understood Teacher Fellow Eric Crouch.
UDLA has technical assistance and PD options that guide teams through the stages of implementation. UDLA provides PD that not only teaches UDL but allows for coaches to practice how they might support teachers in the field. UDL is a research-based framework that places great emphasis on building self-directed learners. Learners will explore the factors that drive motivation and how those can be leveraged in the classroom.
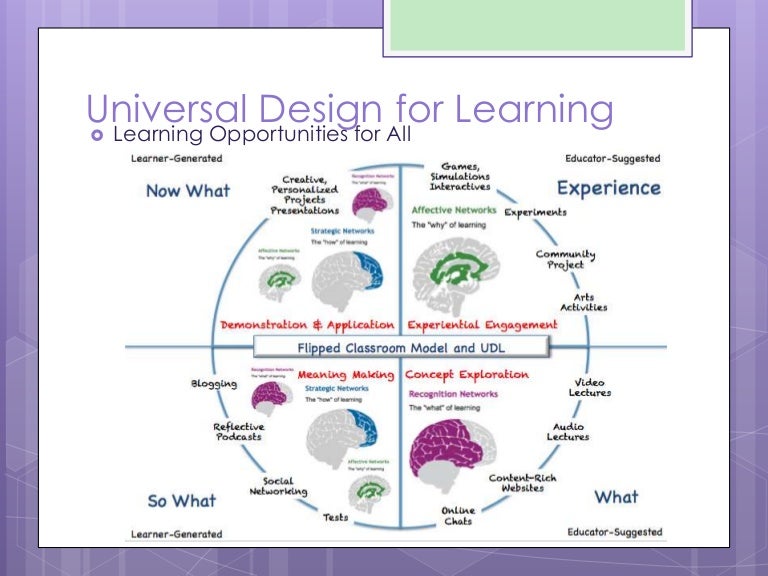
See more on UDL principles and how they can be applied, or use a course accessibility checklist to check how accessible your course is. UDL describes human variability based on parts of the brain that manage the “why” (affective network), the “what” (recognition network), and the “how” (strategic network) of learning. Watch as CAST co-founder David Rose explains why UDL emphasizes variability instead of disability.
This program is designed for working professionals who desire to advance their career in instructional design. Provide multiple means of action and expression for learners to demonstrate what they have learnt. UDLA has options that support self-directed learners (resources, automated course) to more those that prefer more structure and guidance (in-person workshops, moderated online course work).
For purposeful, motivated learners, stimulate interest and motivation for learning. For example, closed captioning is often used in noisy places like restaurants and airports to help everyone follow what’s being said on TV. Even if you’re not familiar with the term universal design, you’ve likely encountered it in your everyday life. Common examples include automatic doors and dictation tools on smartphones. After you apply, the financial aid office will determine your financial need and inform you of the federal or private loans that are available to you.
Series from the EDUCAUSE Learning Initiative (ELI) provides concise information on emerging learning technologies. Each brief focuses on a single technology and describes what it is, where it is going, and why it matters to teaching and learning. You could share a mini-lesson on butterfly metamorphosis and have students use a guided worksheet as they write. Or you could set up stations where students are grouped using flexible grouping around understanding of the topic, language ability, or reading level.
What defines effective implementation of UDL is the establishment of classrooms that welcome and support individuals from varied backgrounds, embracing their unique abilities rather than sidelining them. Educators are encouraged to recognize that students will vary in how they express what they know. UDL's principle of multiple means of action and expression suggests that students should be allowed to demonstrate their understanding in a variety of ways.
Use of these 3 principles by teachers in their curriculum planning practice can optimise learning for all students, not just the mythical ‘average’ learner. Teachers incorporate multiple means to represent lesson content and provide learners with a variety of options demonstrate their learning. Embodied in the mission of UDL is the goal to dismantle learning barriers for all, particularly for students with disabilities. The framework's holistic approach - which encompasses multiple means of representation, action, and engagement - seeks to cater to the diverse needs of learners.

No comments:
Post a Comment